前传参考记一次数值实验的失败。博主没有一口气写过这么多代码,第一次写这么多,人菜请谅解🙏
请电脑端阅读,移动端体验不佳。
本文使用的是旧版图表,可能不够严谨,见谅。
独立完成,有GPT协助学习和检错。
本项目的目的只是为了学习和练习中小项目code的能力。
目前总代码量大致0.6k行左右。
本文大量AI总结,由我整理。
简谈
后悔信了ChatGPT的邪,没有使用指针。现在我手痒难耐,看什么都想*一下。对于std::vector<uint64_t> data而言,如果是一个std::vector<uint64_t>* pData就更好了。现在束手束脚的,GPT评我函数式编程南蚌,什么究极缝合怪,也是没经验的无奈之举。指针可能比较危险,但是用智能指针应该就没有那么危险了,而且有利于未来多线程吧。
算法与实现
设计意图
- 大整数表示与存储:使用
std::vector<uint64_t>分块存储大整数,每块18位。 - 符号管理:用
bool isPositive单独管理正负符号。 - 工厂模式:
create方法用于从字符串创建对象。 - 运算符重载:重载加法、减法、比较运算符,支持直接运算和比较。
- 加减法实现:加法处理进位,减法处理借位,考虑符号。
- 字符串与格式化输出:支持
from_string和to_string,print提供格式化输出。 - 内存管理优化:使用
std::move和std::vector的预分配内存来优化性能。 - 异常处理:
from_string处理非法输入并抛出异常。 函数式编程与面向对象结合:
add和sub函数处理加减法的绝对值部分,减少代码冗余。源码
//NumberEx.h
#ifndef NUMBEREX_H
#define NUMBEREX_H
#include<string>
class NumberEx {
public:
virtual ~NumberEx() = default;
virtual void from_string(const std::string& str) = 0;
virtual std::string to_string() const = 0;
virtual void print(std::string format) const = 0;
};
#endif //NUMBEREX_H//IntEx.h
#ifndef INTEX_H
#define INTEX_H
#include "NumberEx.h"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
class IntEx : NumberEx {
private:
std::vector<uint64_t> data;
bool isPositive;
static constexpr size_t BLOCK_MAX = 18;
IntEx() : isPositive(true), data() {}
IntEx(const std::string& str) {
from_string(str);
}
bool isGreaterThan(const IntEx& other) const;
bool isEqualTo(const IntEx& other) const;
friend IntEx add(const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs1, const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs2);
//要保证abs1大于abs2
friend IntEx sub(const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs1, const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs2);
public:
//工厂模式create方法
static IntEx create(const std::string& str = "0") {
return IntEx(str);
}
void clear();
bool isEmpty();
//拷贝构造函数
IntEx(const IntEx& other) : isPositive(other.isPositive), data(other.data) {}
//移动拷贝函数
IntEx(IntEx&& other) noexcept : isPositive(other.isPositive), data(std::move(other.data)) {}
IntEx abs(void) const;
//重载计算符号
IntEx& operator=(const IntEx& other);
IntEx& operator=(IntEx&& other) noexcept;
IntEx operator+(const IntEx& other) const;
IntEx operator-(const IntEx& other) const;
//重载逻辑判断
bool operator>(const IntEx& other) const;
bool operator<(const IntEx& other) const;
bool operator==(const IntEx& other) const;
bool operator!=(const IntEx& other) const;
bool operator>=(const IntEx& other) const;
bool operator<=(const IntEx& other) const;
//从字符串中读入
void from_string(const std::string& str);
//输出到字符串
std::string to_string() const;
//测试打印,参数"number"或"raw"
void print(std::string format = "number") const;
};
#endif//IntEx.cpp
#include "IntEx.h"
#include <stdexcept>
#include <algorithm>//std::reverse
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
//从字符串读入,高位对高位
void IntEx::from_string(const std::string& str) {
if (str.empty()) {
throw std::invalid_argument("Empty String Found.");
}
if (!isEmpty()) {
clear();
}
isPositive = (str[0] != '-');
std::string absStr = isPositive ? str : str.substr(1);
size_t chunk_size = 18;
std::reverse(absStr.begin(), absStr.end()); // 反转字符串以便从低位到高位处理
size_t num_chunks = (absStr.size() + chunk_size - 1) / chunk_size;
data.reserve(num_chunks); // 为数据预分配空间
// 将字符串分成多个块,每个块最大为 chunk_size 位,转换为 uint64_t 类型
for (size_t i = 0, j = 0; i < absStr.size(); i += chunk_size, j++) {
std::string chunk = absStr.substr(i, chunk_size);
std::reverse(chunk.begin(), chunk.end()); // 反转每个块
data.push_back((uint64_t)std::stoull(chunk)); // 转换为 uint64_t 并存储
}
}
//输出到字符串
std::string IntEx::to_string() const {
std::ostringstream output;
if(!this->isPositive)
output << "-";
constexpr size_t BLOCK_SIZE = 18;
const size_t THIS_SIZE = (*this).data.size();
output << this->data[THIS_SIZE - 1];
if (THIS_SIZE > 1)
{
for (int i = this->data.size() - 2; i > -1; i--) {
uint64_t currentValue = this->data[i];
output << std::setw(BLOCK_SIZE) << std::setfill('0') << currentValue;
}
}
return output.str();
}
//清空至有唯一块且为0
void IntEx::clear() {
data.clear();
isPositive = true;
}
bool IntEx::isEmpty() {
return data.empty();
}
//基础比较函数
bool IntEx::isGreaterThan(const IntEx& other) const {
if (this->isPositive && !other.isPositive) {
return true; // 当前数字是正,另一个是负,当前数字肯定大
}
if (!this->isPositive && other.isPositive) {
return false; // 当前数字是负,另一个是正,当前数字肯定小
}
size_t thisSize = this->data.size();
size_t otherSize = other.data.size();
const std::vector<uint64_t>* pLarger = thisSize > otherSize ? &this->data : &other.data;
const std::vector<uint64_t>* pSmaller = thisSize <= otherSize ? &this->data : &other.data;
// 先比较数据的块大小
if (pLarger->size() > pSmaller->size()) {
return this->isPositive ? pLarger == &this->data : pLarger == &other.data;
}
// 逐块比较,注意从大序号块开始比较
for (int i = pLarger->size() - 1; i > -1; i--) {
if ((*this).data[i] > other.data[i]) {
return this->isPositive; // 当前大
} else if ((*this).data[i] < other.data[i]) {
return !this->isPositive; // 当前小
}
}
return false; // 如果完全相等,返回false
}
bool IntEx::isEqualTo(const IntEx& other) const {
// 如果符号不同,直接返回 false
if (this->isPositive != other.isPositive) {
return false;
}
size_t thisSize = this->data.size();
size_t otherSize = other.data.size();
// 如果块数不同,直接返回 false
if (thisSize != otherSize) {
return false;
}
for (int i = thisSize - 1; i > -1; i--) {
if (this->data[i] != other.data[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 只处理绝对值加法
IntEx add(const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs1, const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs2) {
// 常量:用于控制进位限制
constexpr uint64_t LIMIT = 1000000000000000000ULL;
size_t size1 = abs1.size();
size_t size2 = abs2.size();
const std::vector<uint64_t>* pLarger = size1 > size2 ? &abs1 : &abs2;
const std::vector<uint64_t>* pSmaller = size1 <= size2 ? &abs1 : &abs2;
size_t largerSize = pLarger->size();
size_t smallerSize = pSmaller->size();
IntEx result;
result.data.reserve(largerSize + 1); // 预留空间,可能会有进位
bool isCarry = false;
// 执行相加并考虑进位
for (size_t i = 0; i < smallerSize; ++i) {
uint64_t sum = (*pLarger)[i] + (*pSmaller)[i] + isCarry;
result.data.push_back(sum % LIMIT); // 存储当前块的结果
isCarry = sum >= LIMIT; // 判断是否有进位
}
// 处理较长部分的剩余部分
for (size_t i = smallerSize; i < largerSize; ++i) {
uint64_t sum = (*pLarger)[i] + isCarry;
result.data.push_back(sum % LIMIT); // 存储当前块的结果
isCarry = sum >= LIMIT; // 判断是否有进位
}
// 如果最后有进位,新增一位
if (isCarry) {
result.data.push_back(1);
}
return result;
}
//要保证abs1大于abs2
IntEx sub(const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs1, const std::vector<uint64_t>& abs2) {
constexpr uint64_t LIMIT = 1000000000000000000ULL;
const size_t BLOCK_SIZE = abs1.size();
const size_t SMALL_SIZE = abs2.size();
//初始化结果
IntEx result;
bool isBorrow = false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < SMALL_SIZE; i++) {
if (isBorrow) {
if (abs1[i] < abs2[i] + 1) {
result.data.push_back(LIMIT - abs2[i] - 1 + abs1[i]);
isBorrow = true;
} else {
result.data.push_back(abs1[i] - abs2[i] - 1);
isBorrow = false;
}
} else {
if (abs1[i] < abs2[i]) {
result.data.push_back(LIMIT - abs2[i] + abs1[i]);
isBorrow = true;
} else {
result.data.push_back(abs1[i] - abs2[i]);
isBorrow = false;
}
}
}
for (size_t i = SMALL_SIZE; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i++) {
if (isBorrow) {
if (abs1[i] < 1) {
result.data.push_back(LIMIT - 1 + abs1[i]);
isBorrow = true;
} else {
result.data.push_back(abs1[i] - 1);
isBorrow = false;
}
} else {
for (int j = SMALL_SIZE; j < BLOCK_SIZE; j++) {
result.data.push_back(abs1[j]);
}
break;
}
}
for(int i = result.data.size() - 1; i > -1; i--) {
if (result.data[i] == 0) {
result.data.pop_back();
continue;
}
result.data.shrink_to_fit();
break;
}
return result;
}
IntEx IntEx::abs(void) const {
IntEx result;
result.data = this->data;
return result;
}
IntEx& IntEx::operator=(const IntEx& other) {
if (this!= &other) {
isPositive = other.isPositive;
data = other.data;
}
return *this;
}
IntEx& IntEx::operator=(IntEx&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
isPositive = other.isPositive;
data = std::move(other.data);
}
return *this;
}
IntEx IntEx::operator+(const IntEx& other) const {
if (this->isPositive == other.isPositive) {
// 同号加法
IntEx result = add(this->data, other.data);
result.isPositive = this->isPositive;
return result;
} else {
// 异号加法
bool thisIsLarger = this->abs() > other.abs();
bool otherIsLarger = this->abs() < other.abs();
// 减法:较大数减去较小数
if (thisIsLarger) {
IntEx result = sub(this->data, other.data);
result.isPositive = this->isPositive;
return result;
} else if (otherIsLarger) {
IntEx result = sub(other.data, this->data);
result.isPositive = other.isPositive;
return result;
} else {
IntEx result = create("0");
result.isPositive = true;
return result;
}
}
}
IntEx IntEx::operator-(const IntEx& other) const {
if (this->isPositive == other.isPositive) {
// 同号减法
bool thisIsLarger = this->abs() > other.abs();
bool otherIsLarger = this->abs() < other.abs();
if (thisIsLarger) {
IntEx result = sub(this->data, other.data);
result.isPositive = this->isPositive;
return result;
} else if (otherIsLarger) {
IntEx result = sub(other.data, this->data);
result.isPositive = !this->isPositive;
return result;
} else {
IntEx result = create("0");
result.isPositive = true;
return result;
}
} else {
// 异号减法,相当于加法
IntEx result = add(this->data, other.data);
result.isPositive = this->isPositive;
return result;
}
}
bool IntEx::operator>(const IntEx& other) const {
return isGreaterThan(other);
}
bool IntEx::operator==(const IntEx& other) const {
return isEqualTo(other);
}
bool IntEx::operator!=(const IntEx& other) const {
return !isEqualTo(other);
}
bool IntEx::operator<(const IntEx& other) const {
return !isGreaterThan(other) && !isEqualTo(other);
}
bool IntEx::operator>=(const IntEx& other) const {
return isGreaterThan(other) || isEqualTo(other);
}
bool IntEx::operator<=(const IntEx& other) const {
return !isGreaterThan(other);
}
//格式化测试打印
void IntEx::print(std::string format) const {
if (format == "raw") {
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {
std::cout << data[i] << std::endl;
}
} else if (format == "number") {
std::cout<<to_string()<<std::endl;
} else {
throw std::invalid_argument("IntEx::Print() Argument Missing Or Illegal.");
}
}修改建议
异常处理:
- 异常处理不一致,缺乏明确的错误类型和捕获机制。需要设计自定义异常,明确错误来源。
内存管理与异常安全:
- 没有考虑
std::vector等的异常安全。应使用RAII技术确保异常发生时资源自动管理。
- 没有考虑
默认构造函数:
IntEx的默认构造函数没有直接初始化data,应在构造函数中初始化成员。
对比函数优化:
isGreaterThan和isEqualTo的逻辑重复。可以提取相似代码,减少冗余。
加法/减法逻辑:
operator+和operator-中有重复逻辑,标志位处理复杂,可抽象化或简化。
构造函数与成员初始化:
IntEx的构造函数使用手动调用clear、reserve,可以用初始化列表简化。
std::move使用:- 使用
std::move时需确保成员变量正确转移且不会被意外修改。
- 使用
常量与魔法数字:
LIMIT常量缺乏注释或解释,需明确用途。
性能与内存优化:
std::vector<uint64_t>可以通过合理预分配和减少内存复制提升性能。
参数与返回类型:
- 函数参数应使用
const修饰,避免不必要的修改。
- 函数参数应使用
GMP 更好
- 内存管理优化:高效的内存池策略,减少内存分配和释放。
- 算法优化:使用高效的加减乘除算法(如Karatsuba、FFT)。
- 硬件优化:利用平台特定的指令集加速运算。
- 多精度支持:动态调整精度,避免内存浪费。
- 跨平台优化:在不同平台上进行特定优化。
- 精度与计算优化:减少精度损耗,优化大整数计算。
- 并行计算支持:支持多核并行计算,提升效率。
测试与分析
测试方法
1234567890循环字符串,分别产生10、20、30、50、100、150、200、300、500、1000位数字。分别测试IntEx和GMP的加法与减法,每种数字进行1000轮,取每轮平均时间。
将测试结果格式化输出到文件,进行数值计算拟合。
测试代码
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include "IntEx.h"
#include <gmpxx.h>
std::string generate_test_data(int length) {
std::string result;
std::string base = "1234567890"; // 循环的基础字符串
while (result.size() < length) {
result += base;
}
return result.substr(0, length);
}
void test_addition_gmp(const std::string& num1, const std::string& num2, int iterations, std::ofstream& output) {
mpz_class a(num1);
mpz_class b(num2);
std::chrono::nanoseconds total_duration(0);
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; ++i) {
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
mpz_class sum = a + b;
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
total_duration += std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);
}
// 计算每组的平均时间
auto average_duration = total_duration.count() / iterations;
output << "GMP add average time for " << iterations << " iterations: " << average_duration << " ns\n";
}
void test_addition_intEx(const std::string& num1, const std::string& num2, int iterations, std::ofstream& output) {
IntEx a = IntEx::create(num1);
IntEx b = IntEx::create(num2);
std::chrono::nanoseconds total_duration(0);
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; ++i) {
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
IntEx sum = a + b;
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
total_duration += std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);
}
// 计算每组的平均时间
auto average_duration = total_duration.count() / iterations;
output << "IntEx add average time for " << iterations << " iterations: " << average_duration << " ns\n";
}
bool validate_addition(const std::string& num1, const std::string& num2) {
mpz_class a(num1);
mpz_class b(num2);
mpz_class gmp_result = a + b;
IntEx intEx_a = IntEx::create(num1);
IntEx intEx_b = IntEx::create(num2);
IntEx intEx_result = intEx_a + intEx_b;
return gmp_result.get_str() == intEx_result.to_string(); // 通过字符串比较
}
void test_subtraction_gmp(const std::string& num1, const std::string& num2, int iterations, std::ofstream& output) {
mpz_class a(num1);
mpz_class b(num2);
std::chrono::nanoseconds total_duration(0);
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; ++i) {
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
mpz_class diff = a - b;
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
total_duration += std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);
}
// 计算每组的平均时间
auto average_duration = total_duration.count() / iterations;
output << "GMP sub average time for " << iterations << " iterations: " << average_duration << " ns\n";
}
void test_subtraction_intEx(const std::string& num1, const std::string& num2, int iterations, std::ofstream& output) {
IntEx a = IntEx::create(num1);
IntEx b = IntEx::create(num2);
std::chrono::nanoseconds total_duration(0);
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; ++i) {
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
IntEx diff = a - b;
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
total_duration += std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(end - start);
}
// 计算每组的平均时间
auto average_duration = total_duration.count() / iterations;
output << "IntEx sub average time for " << iterations << " iterations: " << average_duration << " ns\n";
}
bool validate_subtraction(const std::string& num1, const std::string& num2) {
mpz_class a(num1);
mpz_class b(num2);
mpz_class gmp_result = a - b;
IntEx intEx_a = IntEx::create(num1);
IntEx intEx_b = IntEx::create(num2);
IntEx intEx_result = intEx_a - intEx_b;
return gmp_result.get_str() == intEx_result.to_string(); // 通过字符串比较
}
int main() {
std::ofstream output("test_results.txt");
int iterations = 1000;
int lengths[] = {10, 20, 30, 50, 100, 150, 200, 300, 500, 1000};
for (int len : lengths) {
std::string num1 = generate_test_data(len);
std::string num2 = generate_test_data(len);
// 加法测试
output << "Testing addition for numbers of size " << len << "...\n";
test_addition_gmp(num1, num2, iterations, output);
test_addition_intEx(num1, num2, iterations, output);
if (validate_addition(num1, num2)) {
output << "IntEx addition test passed for numbers of size " << len << "\n";
} else {
output << "IntEx addition test failed for numbers of size " << len << "\n";
}
// 减法测试
output << "Testing subtraction for numbers of size " << len << "...\n";
test_subtraction_gmp(num1, num2, iterations, output);
test_subtraction_intEx(num1, num2, iterations, output);
if (validate_subtraction(num1, num2)) {
output << "IntEx subtraction test passed for numbers of size " << len << "\n";
} else {
output << "IntEx subtraction test failed for numbers of size " << len << "\n";
}
}
output.close();
return 0;
}
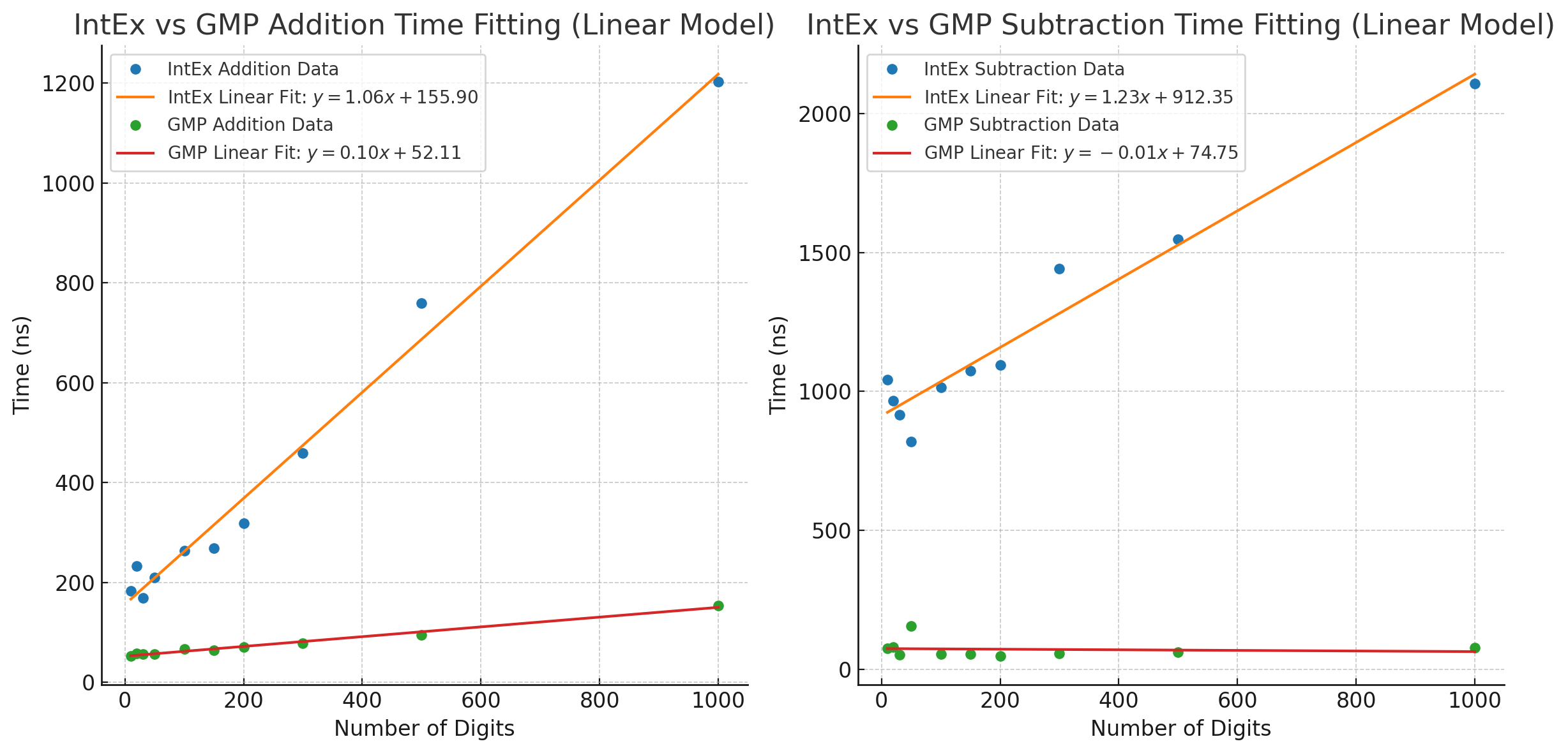
原始数据
| 数字位数 | GMP 加法 (ns) | IntEx 加法 (ns) | IntEx 加法慢百分比 (%) | GMP 减法 (ns) | IntEx 减法 (ns) | IntEx 减法 慢百分比 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 53 | 183 | 244.3% | 75 | 1043 | 1297.3% |
| 20 | 58 | 233 | 301.7% | 81 | 966 | 1092.6% |
| 30 | 56 | 169 | 201.8% | 53 | 915 | 1632.1% |
| 50 | 56 | 210 | 275.0% | 157 | 819 | 421.0% |
| 100 | 67 | 263 | 292.5% | 55 | 1014 | 1734.5% |
| 150 | 64 | 268 | 318.8% | 56 | 1074 | 1825.0% |
| 200 | 71 | 319 | 349.3% | 49 | 1096 | 2122.4% |
| 300 | 78 | 459 | 487.2% | 57 | 1442 | 2424.6% |
| 500 | 95 | 759 | 698.9% | 61 | 1547 | 2451.0% |
| 1000 | 154 | 1203 | 680.5% | 78 | 2108 | 2707.7% |
拟合曲线
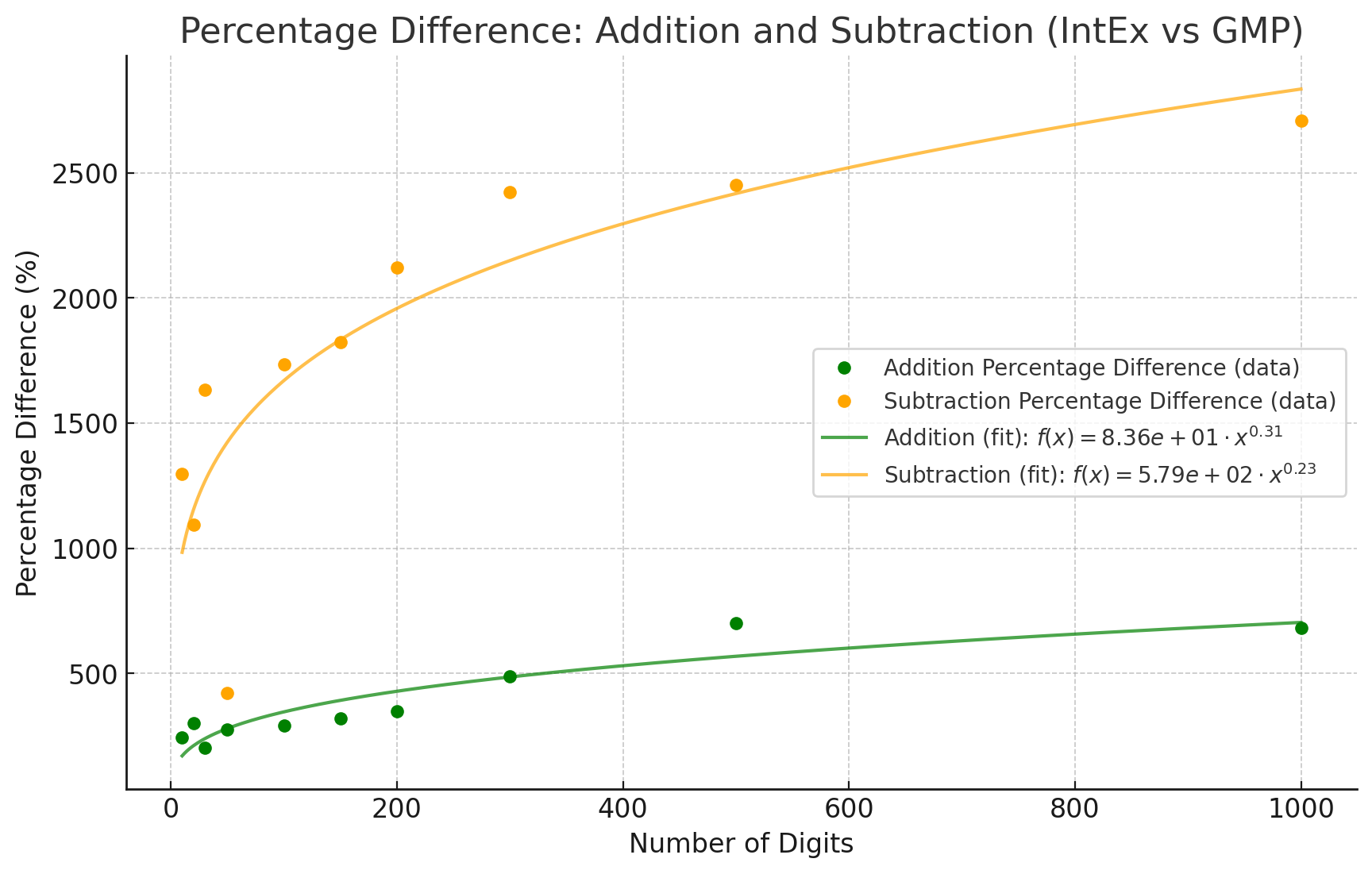
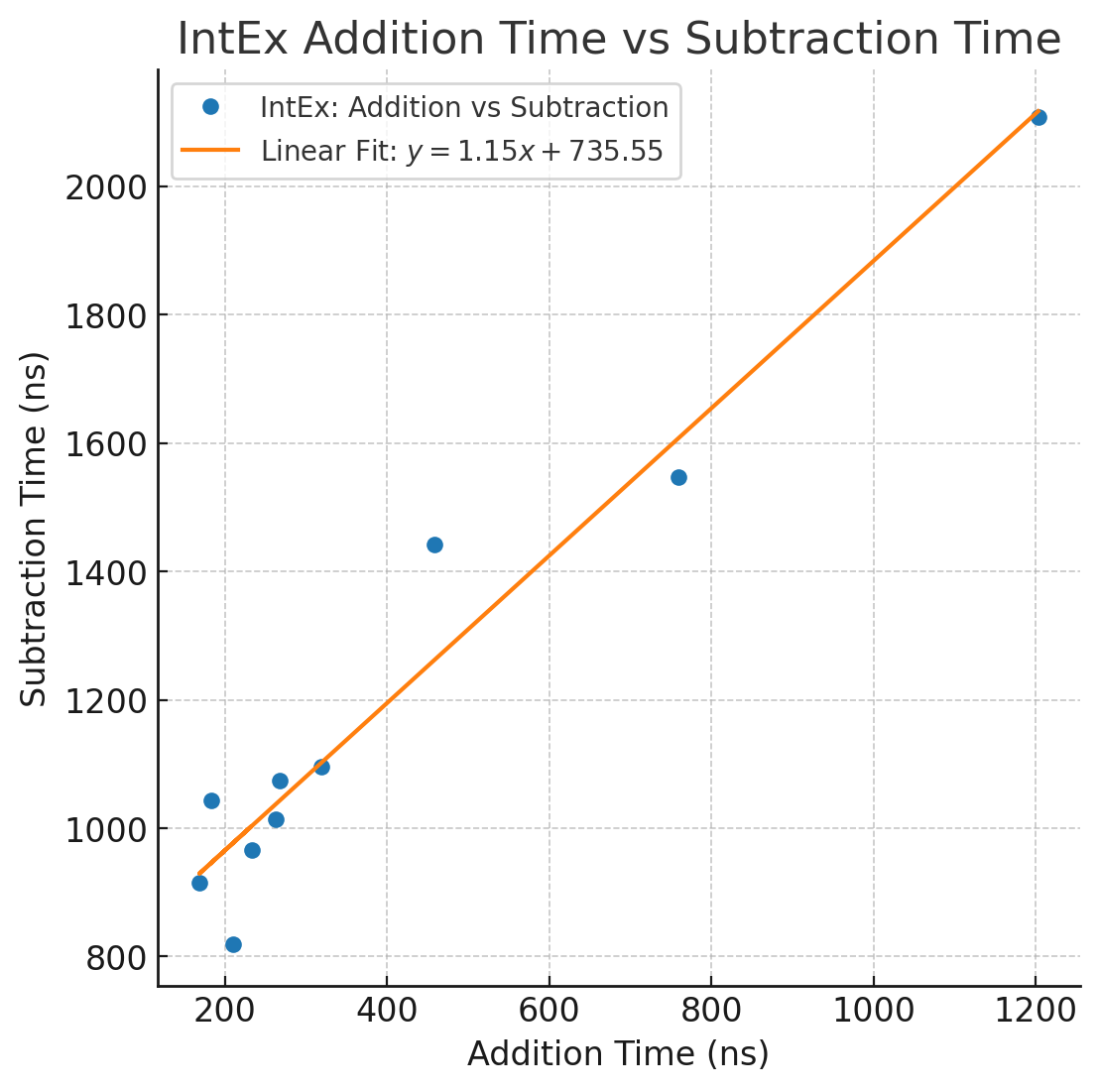
经过数值拟合,得到了以下图像:
结果分析
IntEx各方面都远远差于GMP。
从IntEx的角度看,随着数字位数的增加,加法和减法的执行时间显著增长。例如,10位加法为183纳秒,1000位加法为1203纳秒,增长了约6.57倍;10位减法为1043纳秒,1000位减法为2108纳秒,增长了约2.02倍。总体上,减法操作的执行时间普遍长于加法,10位时减法比加法慢约5.7倍,1000位时慢约1.75倍。随着数字位数的增加,二者的差异逐渐缩小。
与GMP相比,IntEx的加法和减法性能差距逐渐增大,特别是在数字位数较大时。加法的慢百分比从244.3%增加到680.5%,减法的慢百分比从1297.3%增加到2707.7%。这表明IntEx在处理大整数时,性能差距与GMP的差距不断扩大。
遇到的问题
到了喜闻乐见的🤡环节了。
使用了未初始化对象
原来是没写条件分支里的return。我用gdb和valrind测了好久,就是忘了这么简单的事情。
无法利用cmake link GMP
从源文件编译安装的\usr\local\下,对应的目录分别位\usr\local\include\和\usr\local\lib\。
我当然不会蠢到这些都不知道。所以究竟是什么问题让cmake始终无法识别GMP库呢?
我的测试是在项目根目录下的test文件夹独立进行的,自己编写了bash脚本一件编译运行。最新的这些测试都在test中进行,而我抓狂疯狂修改的CMakeLists.txt位于根目录。
🤡
评论区(暂无评论)